Understanding The Full Form Of ASF: A Comprehensive Guide
ASF, or African Swine Fever, has become a significant concern in the global livestock industry. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of ASF, its implications, and how it affects various sectors. By exploring its full form and related aspects, we aim to equip readers with valuable insights into this critical issue.
ASF is not just an abbreviation but represents a complex phenomenon that impacts agriculture, economics, and public health. As the world becomes more interconnected, understanding ASF becomes crucial for stakeholders in the livestock industry and beyond.
This article will delve into the full form of ASF, its origins, symptoms, prevention methods, and global implications. By the end of this guide, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of ASF and its significance in today's world.
Read also:Divine Flaws Exploring The World Of Diva Flawless Onlyfans Content
Table of Contents
- What is ASF?
- History of ASF
- Symptoms of ASF
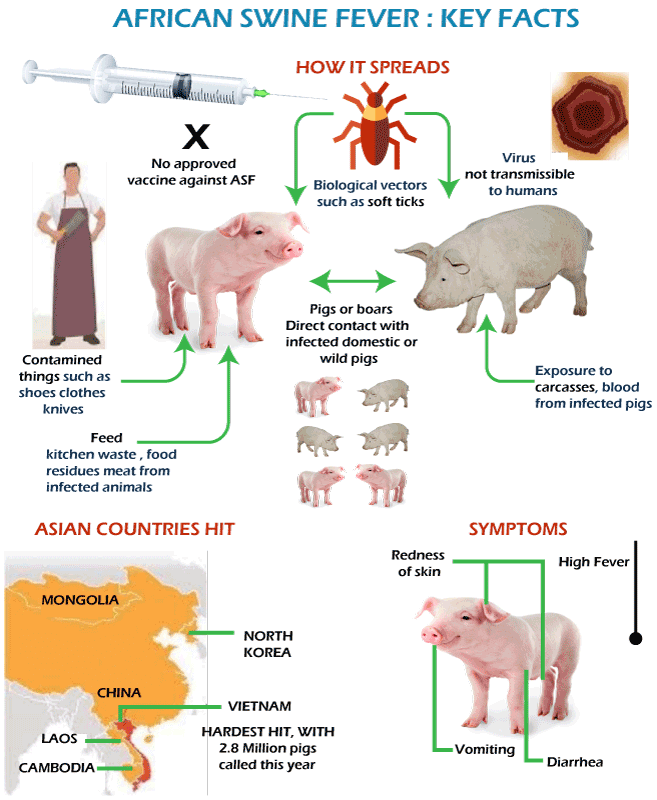
- Transmission of ASF
- Prevention Methods
- Global Impact of ASF
- Economic Effects of ASF
- Control Strategies
- Research and Development
- Conclusion
What is ASF?
ASF stands for African Swine Fever, a highly contagious viral disease that primarily affects domestic and wild pigs. It is caused by the African Swine Fever Virus (ASFV), which belongs to the Asfarviridae family. ASF poses a significant threat to the pig farming industry due to its high mortality rate and lack of available vaccines.
The full form of ASF highlights its origin in Africa, where it was first identified in the early 20th century. Since then, it has spread to various parts of the world, causing widespread economic and ecological disruptions.
Variations of ASF Terminology
While ASF is the most common abbreviation, variations such as "African Pig Fever" or "Swine African Fever" may also be encountered in literature. However, ASF remains the universally accepted term in scientific and agricultural communities.
History of ASF
The history of ASF dates back to the early 1900s when it was first reported in East Africa. Since its discovery, ASF has undergone several outbreaks across continents, impacting both local and global economies.
Key Milestones in ASF History
- 1921: ASF was officially identified in Kenya.
- 1957: The first outbreak outside Africa occurred in Portugal.
- 2007: ASF re-emerged in Georgia, marking the beginning of its spread across Eastern Europe and Asia.
Understanding the historical context of ASF is essential for developing effective strategies to combat its spread.
Symptoms of ASF
ASF symptoms can vary depending on the strain of the virus and the affected pig population. Common symptoms include:
Read also:Unveiling Rei Kamiki A Rising Star In The Spotlight
- High fever
- Loss of appetite
- Weakness
- Bleeding from orifices
- Skin discoloration
In acute cases, ASF can lead to death within a week, while chronic cases may present milder symptoms over a longer period.
Transmission of ASF
ASF spreads through direct contact between infected and healthy pigs. Other modes of transmission include:
- Contaminated feed and water
- Infected ticks (Ornithodoros species)
- Improperly disposed pig products
Preventing the spread of ASF requires strict biosecurity measures and awareness of potential transmission routes.
Role of Ticks in ASF Transmission
Ornithodoros ticks play a crucial role in the transmission of ASF in endemic areas. These ticks act as both hosts and vectors for the ASF virus, complicating efforts to eradicate the disease.
Prevention Methods
Preventing ASF involves a combination of biosecurity measures, education, and policy implementation. Key prevention strategies include:
- Regular health monitoring of pig populations
- Isolation of infected animals
- Proper disposal of carcasses and waste
- Restriction of movement in affected areas
Collaboration between governments, farmers, and international organizations is vital for the successful implementation of these measures.
Global Impact of ASF
ASF has had a profound impact on the global pig farming industry. Countries such as China, Vietnam, and the Philippines have experienced significant losses due to ASF outbreaks. The disease not only affects pig populations but also disrupts supply chains and increases food prices.
ASF in Asia
Since its introduction to Asia in 2018, ASF has caused massive economic losses. China alone has reported a decline in pig populations by over 40%, affecting global pork prices and trade dynamics.
Economic Effects of ASF
The economic impact of ASF extends beyond the livestock industry. Farmers face reduced income, while consumers experience higher meat prices. Additionally, governments allocate significant resources to control outbreaks, further straining national budgets.
Long-term Economic Consequences
Prolonged ASF outbreaks can lead to:
- Shifts in dietary preferences
- Increased reliance on imported meat
- Loss of livelihoods for small-scale farmers
Addressing these economic challenges requires coordinated efforts at both national and international levels.
Control Strategies
Controlling ASF involves a multi-faceted approach that includes:
- Surveillance and early detection
- Quarantine and culling of infected animals
- Research into vaccine development
International cooperation is essential for sharing knowledge and resources to combat ASF effectively.
Role of Technology in Control Strategies
Advancements in diagnostic tools and surveillance technologies have improved the ability to detect and respond to ASF outbreaks. These innovations play a critical role in minimizing the disease's impact.
Research and Development
Research into ASF focuses on understanding the virus's biology, developing effective vaccines, and improving diagnostic methods. Scientists worldwide are working tirelessly to find solutions to this global challenge.
Challenges in Vaccine Development
Developing a vaccine for ASF is complex due to the virus's large genome and diverse strains. However, recent breakthroughs offer hope for the development of a viable vaccine in the near future.
Conclusion
ASF, or African Swine Fever, remains a significant threat to global agriculture and economics. Understanding its full form and implications is crucial for developing effective prevention and control strategies. By implementing robust biosecurity measures, fostering international collaboration, and investing in research, we can mitigate the impact of ASF on pig populations and economies worldwide.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our website for more insights into agricultural and environmental issues. Together, we can work towards a safer and more sustainable future.
Data Sources:
- World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE)
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)